Carbon Film Resistor: The Unsung Hero of Electronics
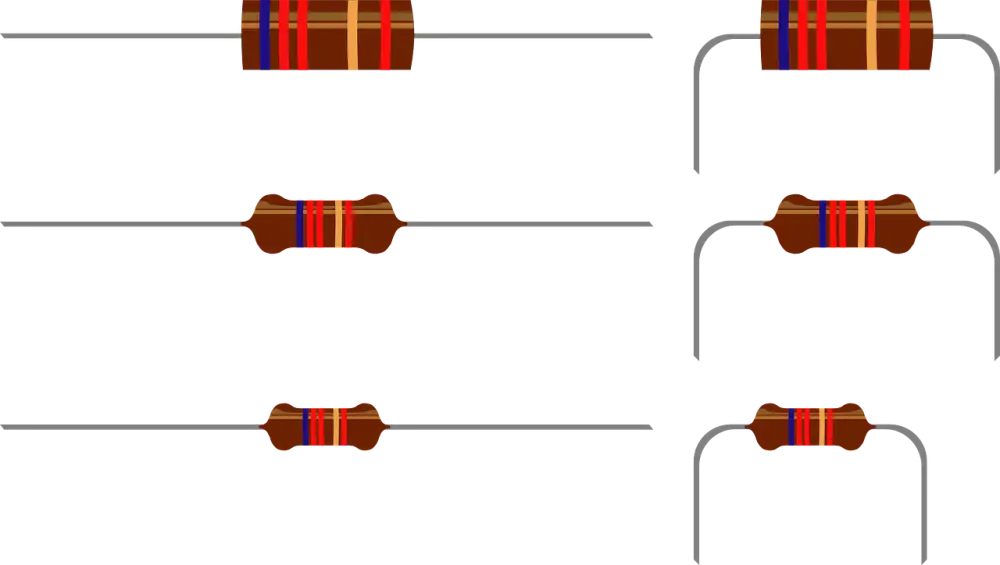
Resistive Element Material
The selection of material for a resistive element depends on the specific application and desired performance characteristics. Common materials include:
Nichrome: This nickel-chromium alloy is widely used due to its high resistivity, good oxidation resistance, and high melting point. It is often found in heating elements, toasters, and hair dryers.
Manganin: This copper-manganese-nickel alloy exhibits a low temperature coefficient of resistance, making it suitable for precision resistors and strain gauges.
Constantan: Similar to manganin, constantan also has a low temperature coefficient of resistance. It is often used in thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs).
Platinum: Known for its high melting point and excellent corrosion resistance, platinum is used in high-temperature applications and specialized resistors.
Carbon: Carbon-based materials, such as carbon film and carbon composition, are used in resistors due to their low cost and wide resistance range. However, they have a higher temperature coefficient of resistance compared to metal alloys.
Construction and Manufacturing
The construction and manufacturing industries are vital components of a thriving economy. Construction involves the creation of infrastructure, buildings, and other physical structures, shaping the landscapes we inhabit. From towering skyscrapers to intricate transportation networks, construction projects drive economic growth and provide essential facilities for our communities. Manufacturing, on the other hand, focuses on transforming raw materials into finished goods. Through sophisticated processes and advanced technologies, manufacturing companies produce a wide range of products, from everyday essentials to complex machinery and electronics. These industries are interconnected, with construction relying on manufactured materials and equipment, and manufacturing often requiring new facilities and infrastructure built by the construction sector.
Resistance Value Determination
Resistors, those little components that manage current flow in circuits, have their resistance measured in ohms (Ω). To figure out a resistor's value, we use a tool called a multimeter. Set the multimeter to the resistance setting (usually denoted by the ohm symbol) and touch the resistor's leads with the multimeter's probes. The multimeter will display the resistance value.
For color-coded resistors, each band of color represents a digit or multiplier. There are handy charts and online calculators available to decode these color bands into the corresponding resistance value. Remember, accurate resistance measurement is crucial in circuit design and troubleshooting to ensure components function correctly.
| Feature | Carbon Film Resistor | Metal Film Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Tolerance | ±5% (typical) | ±1% or better (typical) |
| Temperature Coefficient | -200 to -800 ppm/°C (typical) | ±25 ppm/°C (typical) |
| Cost | Low | Moderate |
| Noise Level | Moderate | Low |
Tolerance and Precision
Tolerance and precision are crucial concepts in various fields, particularly in engineering and manufacturing. Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or property. It defines the acceptable range within which a measurement can deviate from the specified value. Precision, on the other hand, relates to the degree of repeatability or agreement between multiple measurements. It indicates how close these measurements are to each other.
While tolerance and precision are distinct, they are interrelated. High precision often contributes to achieving tight tolerances. When measurements are precise, it becomes easier to manufacture parts within the specified tolerance limits. Conversely, poor precision can make it challenging to meet tolerance requirements, even if the average measurement is within the acceptable range.
Temperature Coefficient
A temperature coefficient describes how much a physical property of a material changes when its temperature is altered by one degree Celsius. This coefficient is crucial in various fields, including electronics and engineering, as it helps predict how materials will behave under different temperature conditions.
For instance, the resistance of a conductor typically increases with temperature, quantified by its temperature coefficient of resistance. Conversely, the energy output of a battery decreases as temperature drops, characterized by its temperature coefficient of voltage. Understanding these coefficients is vital for designing reliable and efficient systems across numerous applications.
Power Rating
A power rating indicates how much energy an electrical device uses or generates. It's measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), where 1 kW equals 1,000 W. Understanding power ratings is crucial for selecting appropriate electrical components, preventing overloads, and estimating energy consumption. Higher wattage usually means more power consumption and potentially higher electricity bills. For example, a 100 W light bulb uses twice the energy of a 50 W bulb over the same period. However, technological advancements, like LED lighting, often provide the same brightness with significantly lower wattage, leading to energy savings. Always check the power rating of devices and appliances to ensure compatibility with your electrical system and manage your energy usage effectively.
Applications and Advantages
They are used in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. In healthcare, they are used to diagnose diseases, develop new treatments, and provide personalized care. In finance, they are used to detect fraud, manage risk, and provide investment advice. In transportation, they are used to optimize logistics, improve traffic flow, and develop autonomous vehicles. The advantages of using these technologies are numerous. They can process large amounts of data quickly and accurately, identify patterns that humans might miss, and automate tasks that are time-consuming or repetitive. They can also help to improve decision-making, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
They are used in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. In healthcare, they are used to diagnose diseases, develop new treatments, and provide personalized care. In finance, they are used to detect fraud, manage risk, and provide investment advice. In transportation, they are used to optimize logistics, improve traffic flow, and develop autonomous vehicles. The advantages of using these technologies are numerous. They can process large amounts of data quickly and accurately, identify patterns that humans might miss, and automate tasks that are time-consuming or repetitive. They can also help to improve decision-making, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
Published: 17. 06. 2024
Category: Food



